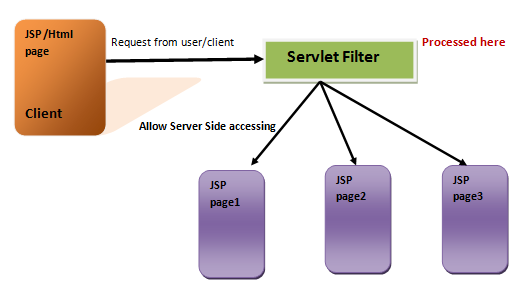
Servlet Filters:
If you are a beginner in web application programming, then
you have a doubt however the user unless logged in to the account access the
resources. Most of the beginners don’t know how solve this problem.This is
avoided by using servlet filters.
The basic functionality of the servlet filter is filtering
the request from the user and allow the access to requested resources.
A filter is an object that performs filtering
tasks on either the request to a resource (a servlet or static content),
or on the response from a resource, or both. Filters perform filtering
in the doFilter method.
Filters are configured in deployment descriptor
file. (web,xml) file.
Filter is a class introduced from servlet2.3 onwards. Controller
first reaches the filter then passes to other resources. Filters are loosely
coupled with the target. (Means, the filter can change without effecting the
any other changes in the code.)
Basic filters are:
1) Authentication
Filters
2) Logging and Auditing Filters
3) Image conversion Filters
4) Data compression Filters
5) Encryption Filters
6) Tokenizing Filters
7) Filters that trigger resource access events
8) XSL/T filters
9) Mime-type chain Filter
Filter enabling in web.xml file
For a specific jsp page use *.jsp
For every request use /*
For a specific jsp page use nameofjsp.jsp
We enable filter functionality by using @WebFilter
annotation. We can create any number of web filters.
Methods in Filter Interface:
init
Called by the web container to indicate to a filter that it is
being placed into service. The servlet container calls the init method exactly
once after instantiating the filter. The init method must complete successfully
before the filter is asked to do any filtering work.
The web container cannot place the filter into service if the init method
either
1.Throws a ServletException
2.Does not return within a time period defined by the web container
Throws:
throws
java.io.IOException,
The doFilter method of the Filter is called by the container each
time a request/response pair is passed through the chain due to a client
request for a resource at the end of the chain. The FilterChain passed in to
this method allows the Filter to pass on the request and response to the next
entity in the chain.
A typical implementation of this
method would follow the following pattern:-
1. Examine the request
2. Optionally wrap the request object with a custom implementation to filter
content or headers for input filtering
3. Optionally wrap the response object with a custom implementation to filter
content or headers for output filtering
4. a) Either invoke the next entity in the chain using the FilterChain
object (chain.doFilter()),
4. b) or not pass on the request/response pair to the next entity in the
filter chain to block the request processing
5. Directly set headers on the response after invocation of the next entity in
the filter chain.
Throws:
java.io.IOException
public void destroy()
Called by the web container to indicate to a filter that it is
being taken out of service. This method is only called once all threads within
the filter's doFilter method have exited or after a timeout period has passed.
After the web container calls this method, it will not call the doFilter method
again on this instance of the filter.
This method gives the filter an opportunity to clean up any resources that are
being held (for example, memory, file handles, threads) and make sure that any
persistent state is synchronized with the filter's current state in memory.
void
|
destroy()
Called by the web
container to indicate to a filter that it is being taken out of service.
|
void
|
doFilter(ServletRequest request, ServletResponse response, FilterChain chain)
The doFilter
method of the Filter is called by the container each time a request/response
pair is passed through the chain due to a client request for a resource at
the end of the chain.
|
void
|
init(FilterConfig filterConfig)
Called by the web
container to indicate to a filter that it is being placed into service.
|
FilterChain is an
interface used to invoke next filter in the chain.
Create a Filter in your web project right click on project and select others, in that select Filter.
See the below
example:
package Filter;
import java.io.IOException;
import javax.servlet.Filter;
import javax.servlet.FilterChain;
import javax.servlet.FilterConfig;
import javax.servlet.ServletException;
import javax.servlet.ServletRequest;
import javax.servlet.ServletResponse;
import javax.servlet.annotation.WebFilter;
/**
* Servlet Filter implementation class FilterDemo
*/
@WebFilter("/FilterDemo")
public class FilterDemo implements Filter {
/**
* Default constructor.
*/
public FilterDemo() {
// TODO Auto-generated constructor stub
}
/**
* @see Filter#destroy()
*/
public void destroy() {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
}
/**
* @see Filter#doFilter(ServletRequest, ServletResponse, FilterChain)
*/
public void doFilter(ServletRequest request, ServletResponse response,
FilterChain chain) throws IOException, ServletException {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
// place your code here
// pass the request along the filter chain
System.out.println(request.getRemoteHost());
chain.doFilter(request, response);
}
/**
* @see Filter#init(FilterConfig)
*/
public void init(FilterConfig fConfig) throws ServletException {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
}
}
Configuring the
filters in web.xml file:
To configure
a filter:
- Open the
web.xml deployment descriptor in a text
editor or use the Administration Console. The web.xml file is located in the WEB-INF directory of your Web
application.
- Add a filter
declaration. The
<filter> element declares a filter,
defines a name for the filter, and specifies the Java class that executes
the filter. The <filter> element must directly follow the
<context-param> element and directly precede the
<listener> and <servlet> elements. For example:
<context-param>Param</context-param>
<filter>
<icon>
<small-icon>MySmallIcon.gif</small-icon>
<large-icon>MyLargeIcon.gif</large-icon>
</icon>
<filter-name>myFilter</filter-name>
<display-name>My Filter</display-name>
<description>This is my filter</description>
<filter-class>examples.myFilterClass</filter-class>
</filter>
<listener>Listener</listener>
<servlet>Servlet</servlet>
The icon, description, and display-name elements are
optional.
- Specify one
or more initialization attributes inside a
<filter> element. For example:
<filter>
<icon>
<small-icon>MySmallIcon.gif</small-icon>
<large-icon>MyLargeIcon.gif</large-icon>
</icon>
<filter-name>myFilter</filter-name>
<display-name>My Filter</display-name>
<description>This is my filter</description>
<filter-class>examples.myFilterClass</filter-class>
<init-param>
<param-name>myInitParam</param-name>
<param-value>myInitParamValue</param-value>
</init-param>
</filter>
Your Filter class can
read the initialization attributes using the FilterConfig.getInitParameter() or FilterConfig.getInitParameters() methods.
- Add filter
mappings. The
<filter-mapping> element specifies which filter
to execute based on a URL pattern or servlet name. The <filter-mapping> element must immediately follow
the <filter> element(s).
- To create a
filter mapping using a URL pattern, specify the name of the filter and a
URL pattern. For example, the following
filter-mapping maps myFilter to
requests that contain /myPattern/.
<filter-mapping>
<filter-name>myFilter</filter-name>
<url-pattern>/myPattern/*</url-pattern>
</filter-mapping>
- To create a
filter mapping for a specific servlet, map the filter to the name of a
servlet that is registered in the Web application. For example, the
following code maps the
myFilter filter to
a servlet called myServlet:
<filter-mapping>
<filter-name>myFilter</filter-name>
<servlet-hame>myServlet</servlet-name>
</filter-mapping>
Configuring a Chain of Filters
WebLogic Server creates a chain of filters by creating a list of all the filter
mappings that match an incoming HTTP request. The ordering of the list is
determined by the following sequence:
- Filters
where the
filter-mapping element contains a url-pattern that matches the request are added
to the chain in the order they appear in the web.xml deployment descriptor.
- Filters
where the
filter-mapping element contains a servlet-name that matches the request are
added to the chain after the filters that match
a URL pattern.
- The last
item in the chain is always the originally requested resource.
In your filter class, use the FilterChain.doFilter() method to
invoke the next item in the chain.